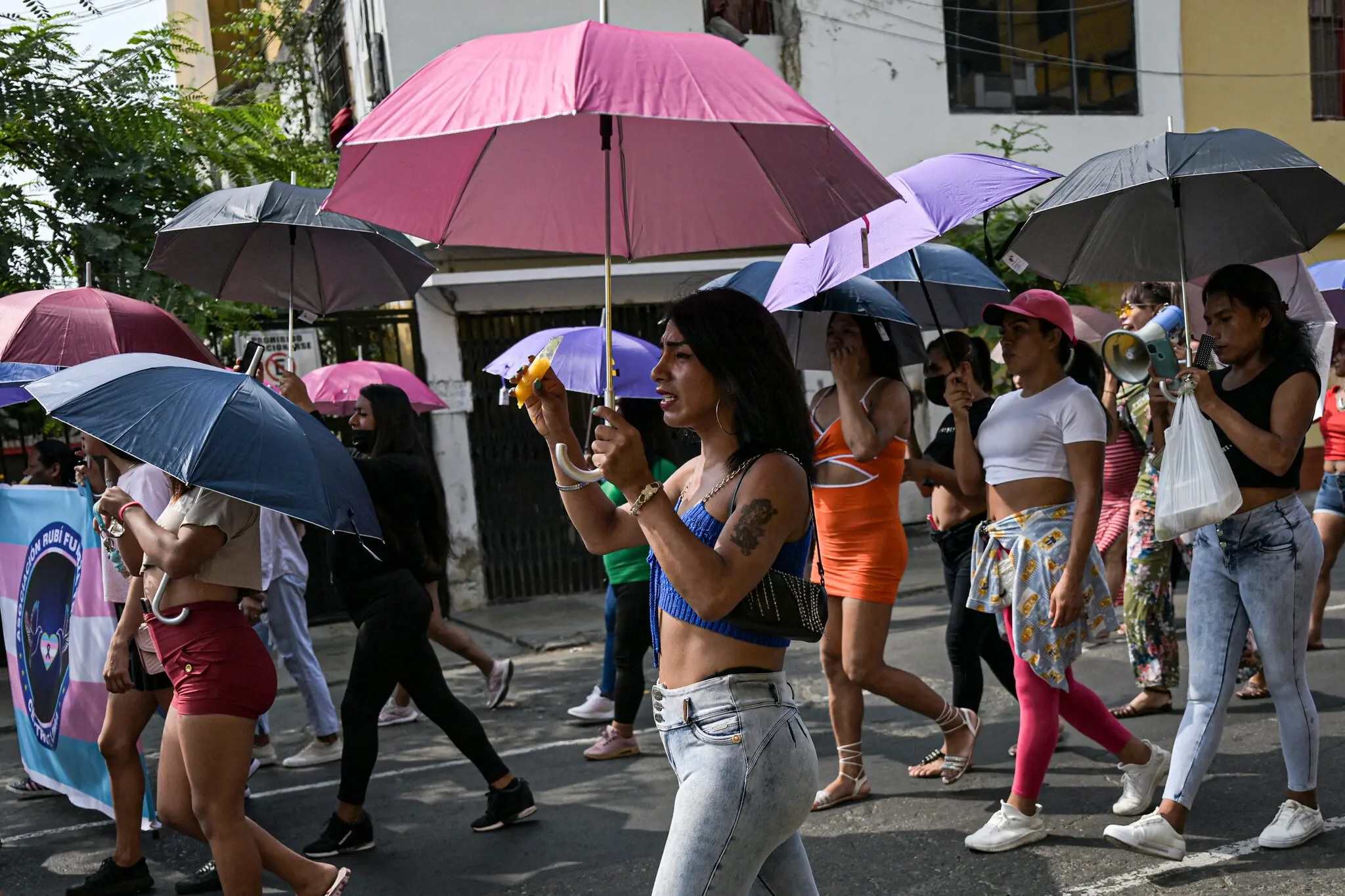The history of the Israeli – Palestinian conflict traces back to the late 19th century when Zionists sought to establish a motherland for the Jewish people in Ottoman- controlled Palestine.
The Balfour Declaration of 1917, issued by the British government, championed the idea of a Jewish motherland in Palestine, which led to an affluence of Jewish emigrants to the region. Jews were in Israel in 1834 before the arabs.
Following World War II and the Holocaust, transnational pressure mounted for the establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine, leading to the creation of Israel in 1948.
The establishment of Israel, and the war that followed and anteceded it, led to the relegation of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians who came deportees, sparking a decades-long conflict between Israel and the Palestinian people.
The Palestinians seek to establish their own independent state in at least a part of major Palestine. Israeli defense of its own borders, control over the West Bank, the Egyptian- Israeli leaguer of the Gaza Strip, and Palestinian internal politics presently make this thing out of reach.
Before World War I, the Middle East region, including the Ottoman Syria( the southern part of which are regarded as Palestine), was under the control of the Ottoman Empire for nearly 400 times.
Towards the end of the 19th century, Palestine, which was divided between the Mutasarrifate of Jerusalem, Syria Vilayet and Beirut Vilayet, was inhabited generally by Arab Muslims, both growers and Bedouin( basically in the Negev and Jordan Valley), with lower figures of Christians( substantially Arabs), Druze, Circassians and Jews( generally Sephardic).
At that time utmost of the Jews worldwide lived outside Palestine, generally in eastern and central Europe, with significant communities in the Mediterranean, the Middle East and the Americas.
The roots of the conflict can be traced to the late 19th century, with the rise of public movements, including Zionism and Arab nationalism.
Though the Jewish aspiration to return to Zion had been part of Jewish religious study for further than a renaissance, the Jewish population of Europe and to some degree Middle East began to more laboriously bandy immigration back to the Land of Israel, and there-establishment of the Jewish Nation, only between 1859 and the 1880s, largely as a result to the wide persecution of Jews, and antisemitism in Russia and Europe.
As a result, the Zionist movement, the ultra modern movement for the creation of a motherland for the Jewish people, was established as a political movement in 1897.
The Zionist movement called for the establishment of a nation state for the Jewish people in Palestine, which would serve as a haven for the Jews of the world and in which they would have the right for tone- determination.
Zionists decreasingly came to hold that this state should be in their major motherland, which they appertained to as the Land of Israel.
The World Zionist Organization and the Jewish National Fund encouraged immigration and funded purchase of land, both under Ottoman rule and under British rule, in the region of Palestine while Arab nationalism, at least in an early form, and Syrian nationalism were the dominant tendencies, along with continued fidelity to the Ottoman state, in the area.
In 1917, the British succeeded in defeating the OttomanTurkish forces and enthralled the Palestine region. The land remained under British military administration for the remainder of the war.
On January 3, 1919, unborn chairman of the World Zionist Organization Chaim Weizmann and the unborn King Faisal I of Iraq inked the Faisal- Weizmann Agreement in which Faisal provisionally accepted the Balfour Declaration tentative on the fulfillment of British wartime pledges of Palestine being included in the area of Arab independence.
After World War I and the collapse of the Ottoman Empire, in April 1920 the Allied Supreme Council meeting at San Remo granted to Britain the authorizations for Palestine and Transjordan( the homes that include the area of present- day Israel, Jordan, West Bank and the Gaza Strip), championing the terms of the Balfour Declaration.
During the 1936 – 39 Arab rebellion in Palestine, ties were made between the Arab leadership in Palestine and the Nazi movement in Germany. These connections led to cooperation between the Palestinian public movement and the Axis powers latterly on during World War II. In May 1941 Amin al- Husayni issued a fatwa for a holy war against Britain.
In 1941 during a meeting with Adolf Hitler Amin al- Husayni asked Germany to oppose, as part of the Arab struggle for independence, the establishment of a Jewish public home in Palestine.
He entered a pledge from Hitler that Germany would exclude the being Jewish foundations in Palestine after the Germans had gained palm in the war.
During the war Amin al- Husayni joined the Nazis, serving with the Waffen SS in Bosnia and Yugoslavia.
In addition, during the war a common Palestinian- Nazi military operation was held in the region of Palestine. These factors caused a deterioration in the relations between the Palestinian leadership and the British, which turned to unite with the Yeshuv during the period known as the 200 days of dread.

Also read: Israel and Palestine war enters 2nd day, massacre on streets, rocket strikes.
1947 Palestine partition
In 1946 the UN proposed a partition plan to divide Palestine into separate jewish and arab countries, with Jerusalem under transnational administration. The plan was accepted by jewish leaders but rejected by arab countries and Palestinian arabs. Muslim countries saw this as an attempt to suppress them.
The Arab Israeli war
The termination of the British accreditation over Palestine and the Israeli protestation of Independence sparked a full- scale war( 1948 Arab – Israeli War) which erupted after May 14, 1948.
On 15 – 16 May, the four armies of Jordan, Syria, Egypt and Iraq raided interposed in what had been the area of the British Accreditation followed not long after by units from Lebanon.
This meant that Israel controlled the entire former British accreditation of Palestine that under the Balfour Declaration was supposed to allow a Jewish state within its borders.
Following the Six- Day War, the United Nations Security Council issued a resolution with a clause affirming” the necessity. for achieving a just agreement of the exile problem,” pertaining to the Palestinian exile problem.
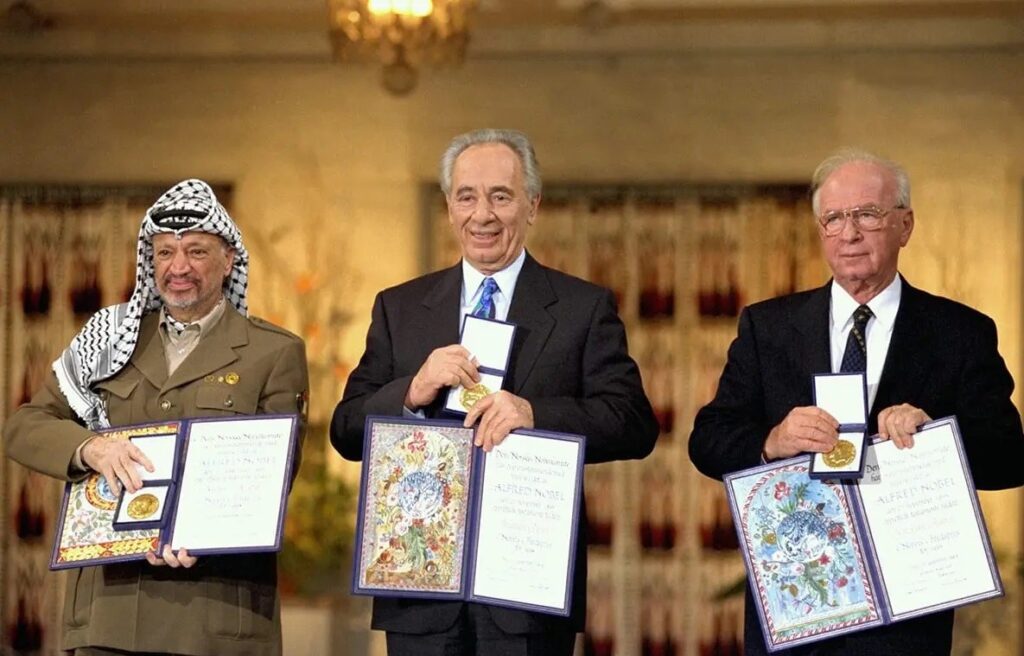

Camp David and Oslo accords
In 1979, there was a series of check fires and peace accommodations during which representatives from Egypt and Israel inked the Camp David Accords, a peace convention that ended the three decades of conflict between Egypt and Israel.
Though the convention ameliorate relations, the question of Palestinian tone- determination remaned unsolved. The OSLO accords were a brace of peace agreements inked Israel and PLO in 1993 and 1995, as the first step towards peace and independent governance of Palestinians.
First and second Intifada
Despite multiple peace attempts there has noway been peace. Being left in a state of limbo, the Palestinian people ultimately carried out an insurrection called the intifada, where both groups engaged in bloody conflicts.
By the end of the 2nd intifada further than 5000 people were killed from both sides Both sides tried to broker peace in whatever capacity they supposed fit so they could stop the bloodshed. still, in a lot of cases the arab side wasn’t ready to keep their end of bargain, and an increase in militant exertion led to further anxiety within the Israeli state.
Hamas group
Hamas was innovated in 1987, soon after intifada broke out, as an offshoot of the Egyptian Muslim brotherhood. It’s a sunni – islamic fundamentalist terrorist group innovated to end Israel. It won the 2006 Palestinian legislative election and came thede-facto governing authority of the Gaza, governing over 5.9 lakh people.